Global Gender Gap Index
- The Global Gender Gap Index for the year 2020 was released by World Economic Forum.
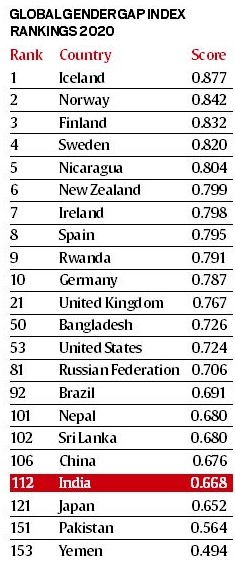
- Iceland, Norway, and Finland occupy the top three spots in the Report. Yemen ranked at the last place (153rd).
- India has ranked 112th among 153 countries, slipped four places from the previous year ranking.
- Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka and China are ranked at 50, 101, 102 and 106respectively. Pakistan is ranked at 151.
- It measures progress towards parity between men and women in –
1. Economy
2. Education
3. Health &
4. Political representation.
- The index lies between 0 and 1, with 1 denoting complete parity and 0, complete inequality.
- Key Findings – The largest gender disparity is in political empowerment.
- Only 25% of the total seats in parliaments around the world are occupied by women, and only 21% of the ministers are women.
- By following the current trends, the overall global gender gap will close in 99.5 years.
- It can potentially be closed 71.5 years in South Asia.
- Globally, the average distance completed to gender parity is at 68.6%, which is an improvement since last edition.
- India – Ranked 18th in political empowerment and 4th in the number of years a female or a male ruled a state.
- Ranked in the bottom-five in terms of women’s health and survival and economic participation.
- On health and survival, four large countries such as Pakistan, India, Vietnam and China fare badly with millions of women not getting the same access to health as men.
- It has closed two-thirds of its overall gender gap (score of 66.8%)
Other Gender Related Reports
- The Gender Parity Index is released by UNESCO.
- The Gender Inequality Index is released by UNDP.